
Overview of AWS’s New Security Enhancement
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has recently enhanced its Key Management Service (KMS), Certificate Manager (ACM), and Secrets Manager by integrating the ML-KEM post-quantum key encapsulation mechanism. This significant update makes TLS connections more secure against future quantum computing threats.
Understanding ML-KEM
ML-KEM, or Module-Lattice-based Key Encapsulation Mechanism, is a cutting-edge cryptographic algorithm developed to protect key exchanges from the potential risks posed by quantum computers. These quantum devices could potentially decrypt existing encryption methods such as RSA and elliptic curve cryptography (ECC).
The algorithm is rooted in CRYSTALS-Kyber, a key player in the post-quantum cryptography field chosen by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) for its standard framework, finalized in August 2024.
Strategic Implementation and Future Planning
Although quantum computers do not currently threaten modern cryptography, AWS is taking proactive steps to secure against future vulnerabilities through these quantum-resistant algorithms. This strategic foresight aids in preventing future “harvest now, decrypt later” attacks, where adversaries collect encrypted data to decrypt once the technology becomes available.
- ML-KEM is now supported across AWS’s KMS, ACM, and Secrets Manager.
- Support for its predecessor, CRYSTALS-Kyber, will continue through 2025 and will be phased out by 2026.
Activating ML-KEM in AWS Services
To utilize ML-KEM’s post-quantum TLS capabilities, users of AWS services such as KMS, ACM, or Secrets Manager need to update their client SDKs and enable the specific feature. AWS provides guidelines for configuring ML-KEM, accessible to both Java SDK users (version 2.30.22 onwards) and Rust SDK users.
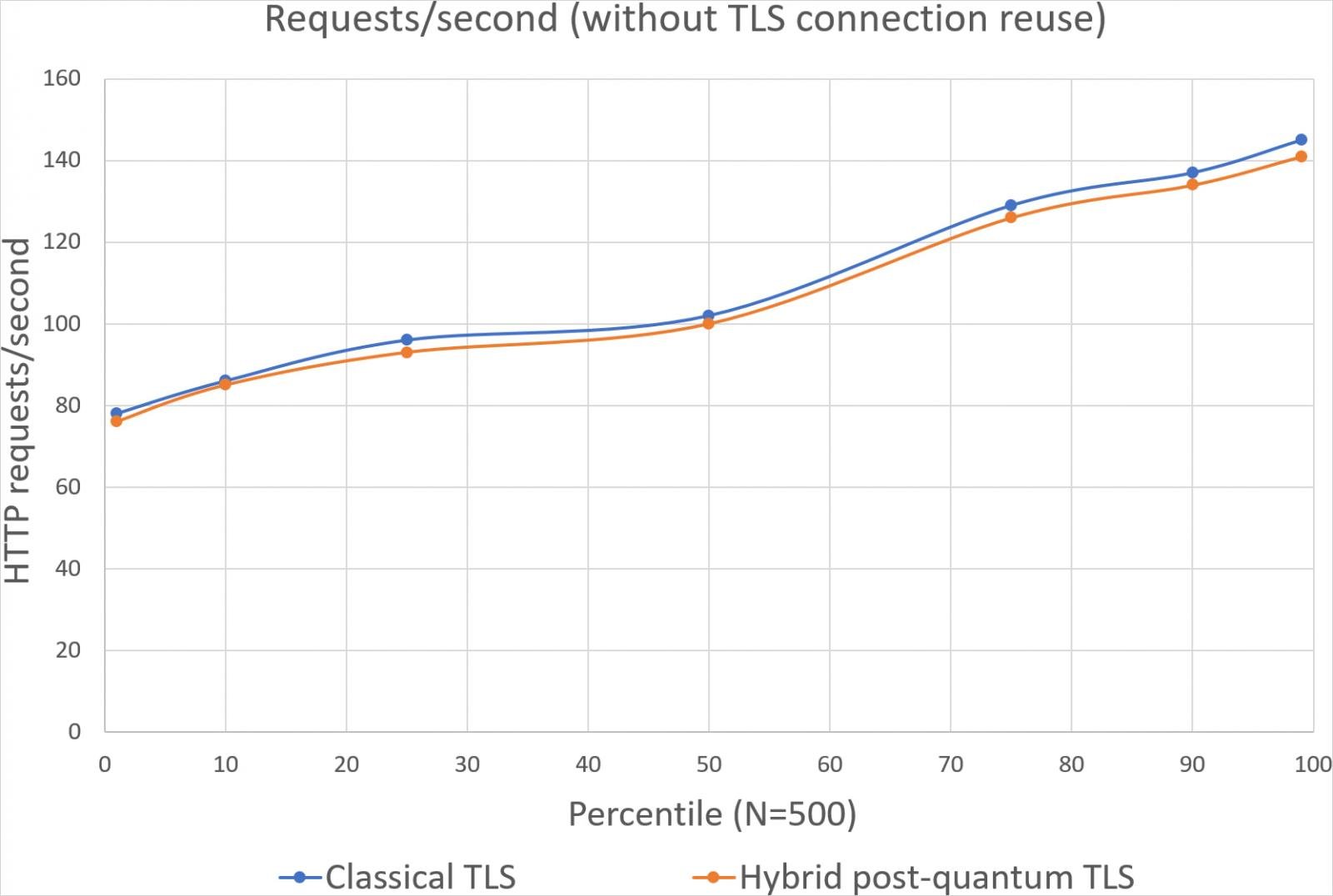
Performance Impact and Recommendations
AWS reports that the impact on performance when enabling ML-KEM is minimal, encouraging users to adopt this advanced security measure. The results from AWS’s benchmarks underline the efficiency of ML-KEM even in intensive scenarios:
- With TLS connection reuse, there’s virtually no performance degradation, measured at a mere 0.05%.
- Without reuse, performance decreases by about 2.3%, mainly due to an additional 1,600 bytes in the TLS handshake.
AWS advises administrators to conduct load tests, benchmarks, and connectivity tests to assess the feature’s compatibility and performance in their specific environments.
Leveraging AWS’s instructions, users can ensure that their applications are shielded against prospective quantum-level threats, with little to no compromise on performance.

Source: AWS
Related: Critical Alert: How the Latest FortiSwitch Vulnerability Could Compromise Your Network
Last Updated: April 8, 2025




